🔒 Security
Do not expose WhatsApp API on public networks!
We do not recommend exposing the API on any public networks!
Either protect the API with Api Key or deny access by using firewalls.
API security
You can protect the API by requiring X-Api-Key header in HTTP request.
You can use WAHA_API_KEY environment variable. It accepts two formats:
WAHA_API_KEY=sha512:{SHA512_HEX_HASH}: requireX-Api-Key: {PLAIN_KEY}header in all requests to the API. This is the recommended format as it stores only the hash of your key in the environment variables, making it more secure if your environment variables are exposed.WAHA_API_KEY={PLAIN_KEY}: requireX-Api-Key: {PLAIN_KEY}header in all requests to the API. This format stores your key in plain text in the environment variables, which is less secure.
Generate and Hash Api-Key
- Generate Api Key using uuid4 and remove
-from it (or find a tool online)
uuidgen | tr -d '-'
> 00000000000000000000000000000000- Hash it using sha512 (or find a tool online)
echo -n "00000000000000000000000000000000" | shasum -a 512
> 98b6d128682e280b74b324ca82a6bae6e8a3f7174e0605bfd52eb9948fad8984854ec08f7652f32055c4a9f12b69add4850481d9503a7f2225501671d6124648 -0000...0000- Api Key that you need to send inX-Api-Keyheader, keep it in secret.98b6...24648- SHA512 hash in hex format. You can set it inWAHA_API_KEY=sha512:{HASH}
Set Api-Key Hash
Set
WAHA_API_KEY=sha512:{SHA512_HEX_HASH} in docker (or in docker-compose.yaml or .env):
docker run -it -e WAHA_API_KEY=sha512:98b6d128682e280b74b324ca82a6bae6e8a3f7174e0605bfd52eb9948fad8984854ec08f7652f32055c4a9f12b69add4850481d9503a7f2225501671d6124648 devlikeapro/waha-plusTest API works as expected
# No Key
curl http://localhost:3000/api/sessions
> {"message":"Unauthorized","statusCode":401}
# Wrong Key
curl -H 'X-Api-Key: othersecret' http://localhost:3000/api/sessions
> {"message":"Unauthorized","statusCode":401}
# Right Key
curl -H 'X-Api-Key: 00000000000000000000000000000000' http://localhost:3000/api/sessions
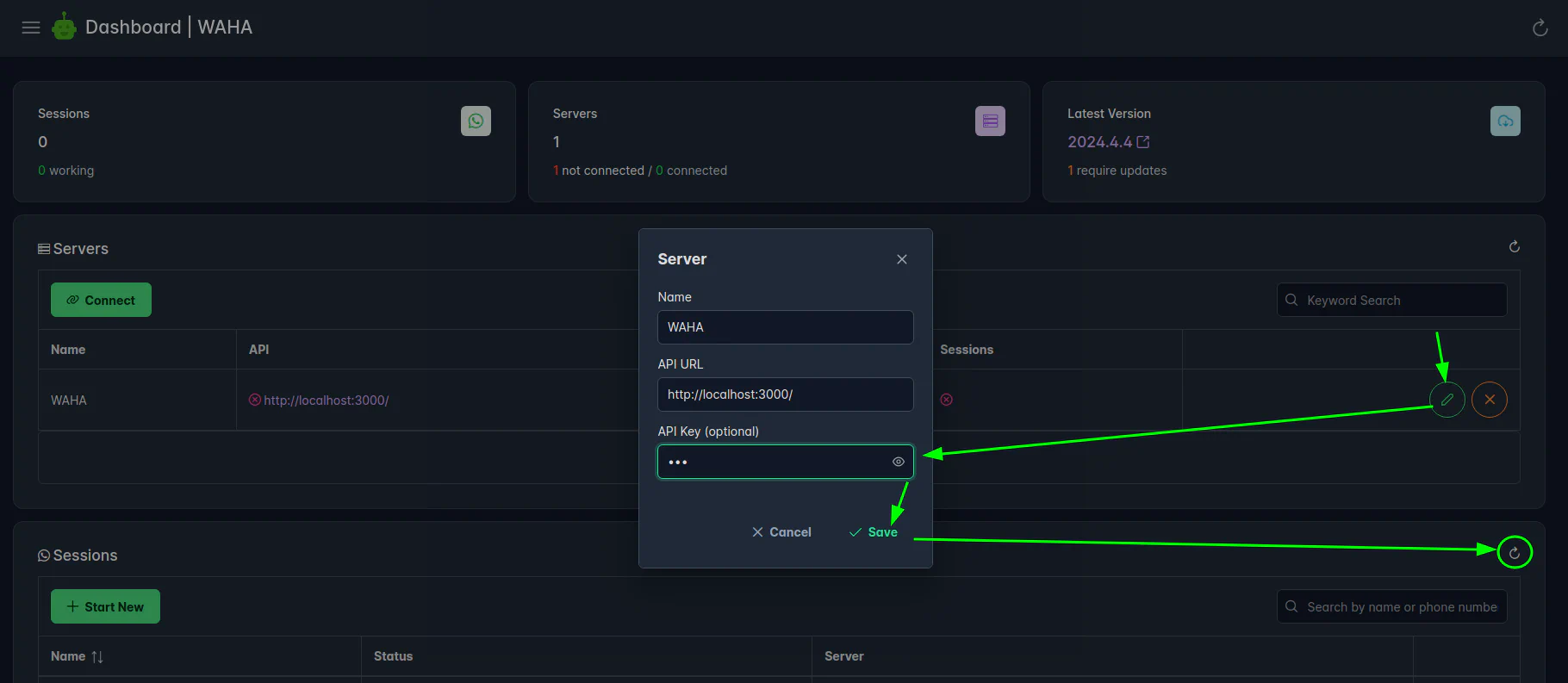
> []Use Api-Key in Dashboard
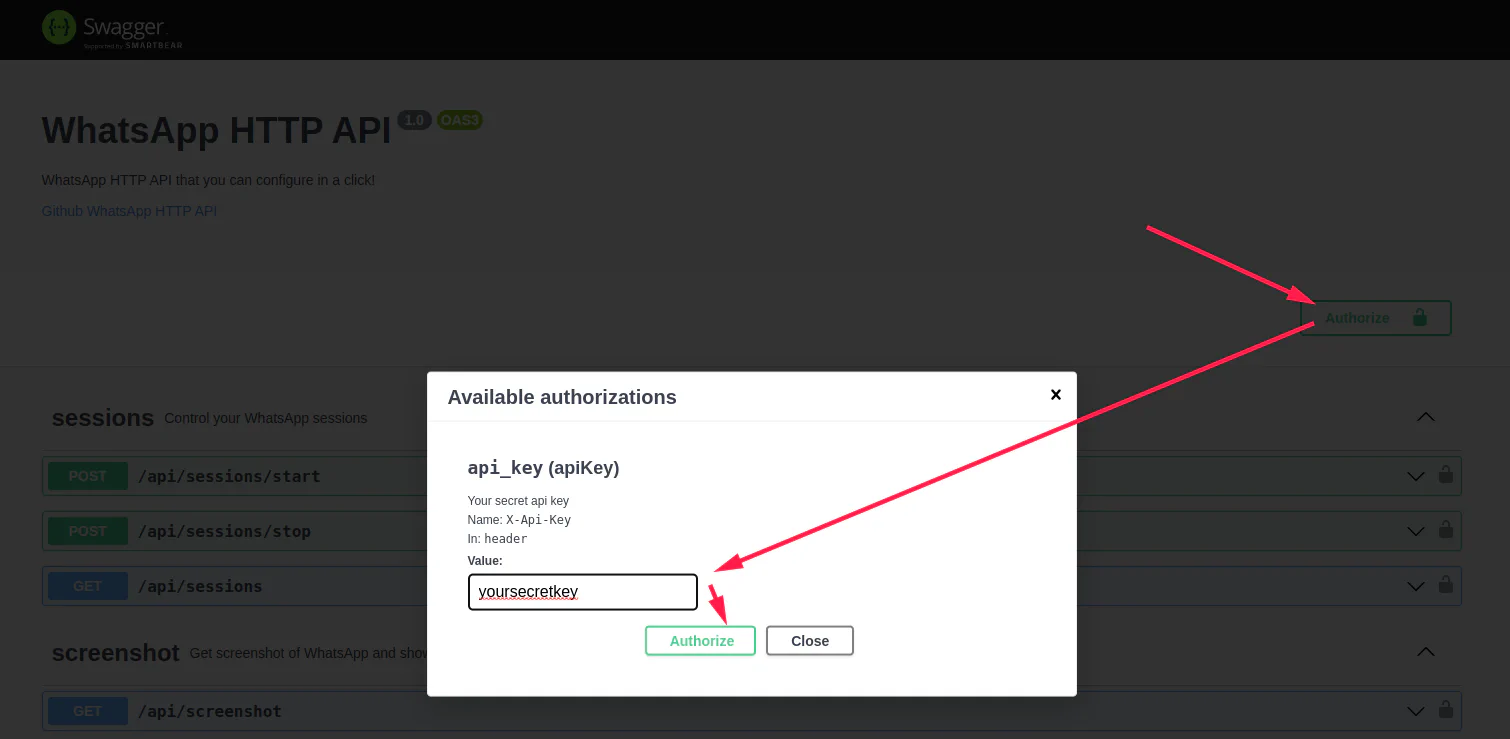
Use Api-Key in Swagger
After you set Api Key - to authorize on swagger, use the Authorize button at the top:
Use X-Api-Key in HTTP request
To authorize requests - set X-Api-Key header to yoursecretkey for all requests that go to WAHA.
Exclude endpoints
If you need to exclude some endpoints (like GET /health or GET /ping) from the API Key requirement - you can
set WAHA_API_KEY_EXCLUDE_PATH environment variable with a comma-separated list of endpoints (no / at the beginning).
docker run -it \
-e WAHA_API_KEY_EXCLUDE_PATH="health,ping" \
-e WAHA_API_KEY=yoursecretkey \
devlikeapro/waha-plusSwagger Security
If you want to hide the project Swagger panel under the password - run the following command to hide under admin/admin
login and password.
docker run -it -e WHATSAPP_SWAGGER_USERNAME=admin -e WHATSAPP_SWAGGER_PASSWORD=admin devlikeapro/waha-plusOpen http://localhost:3000/ and enter admin / admin in the inputs:
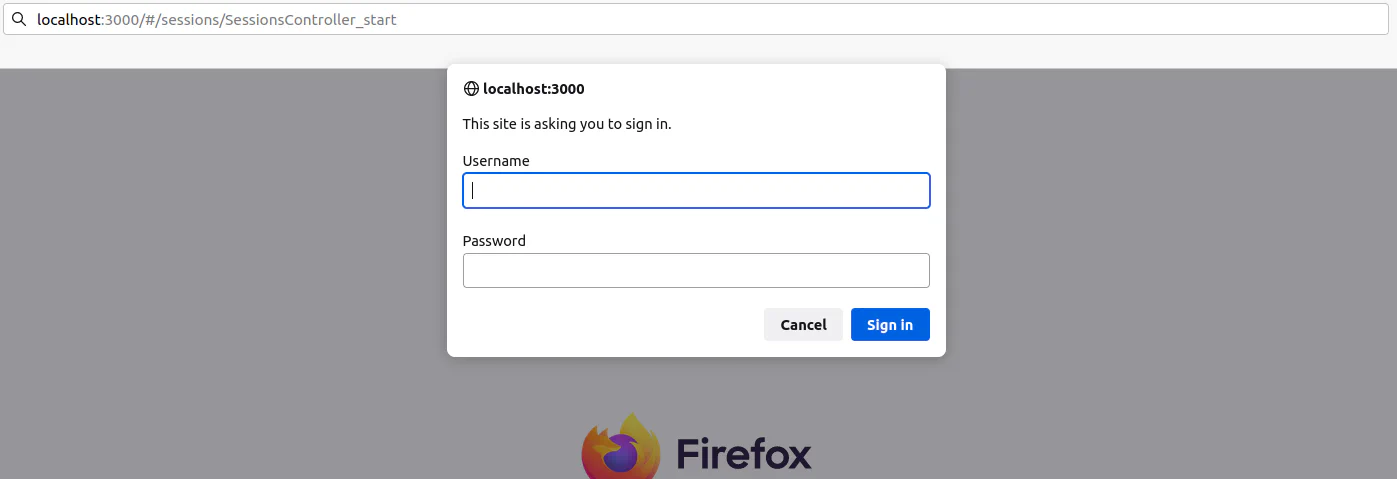
Protecting Swagger under the password does not protect your API from other request! Use both techniques to protect your API and Swagger!
Environment variables:
WHATSAPP_SWAGGER_ENABLED=true: Toggle to enable or disable the Swagger.WHATSAPP_SWAGGER_USERNAME=adminWHATSAPP_SWAGGER_PASSWORD=adminSwagger panel withadmin / admincredentials. This does not affect API access.
You can also set Swagger White Label options instead of hiding the Swagger panel.
Dashboard Security
Read more about 📊 Dashboard
When running WAHA you can set the following environment variables to configure the dashboard:
WAHA_DASHBOARD_ENABLED=true- enable or disable the dashboard, by defaulttrue. Set tofalseto disable the dashboard.WAHA_DASHBOARD_USERNAME=waha- username used to log in, by defaultadminorwahaWAHA_DASHBOARD_PASSWORD=waha- password used to log in, by defaultadminorwaha.
Webhook security
To make sure that you get a webhook from your WAHA instance - you can use HMAC authentication.
Read more about 🔄 Events.
HTTPS
After you set up the security options - you should set up HTTPS to protect the data in transit and prevent Man-in-the-middle attacks.
That’s fine to run it on the local network without HTTPS, but for the production environment, HTTPS is a must-have.
Use Nginx to handle HTTPS
We recommend handling HTTPS termination with a reverse proxy like Nginx.
Follow 🔧 Install & Update - Nginx to set up Nginx with Let’s Encrypt.
WAHA supports HTTPS out of the box if you don’t want to use a reverse proxy like Nginx (using Nginx is recommended)
You can set up the following environment variables to enable HTTPS:
WAHA_HTTPS_ENABLED=true: Set this variable totrueto enable HTTPS. By default, it’sfalse.WAHA_HTTPS_PATH_KEY=/path/to/key.pem: The path to the key file for HTTPS. By default./.secrets/privkey.pemWAHA_HTTPS_PATH_CERT=/path/to/cert.pem: The path to the certificate file for HTTPS. By default./.secrets/cert.pemWAHA_HTTPS_PATH_CA=/path/to/ca.pem: The path to the CA file for HTTPS. By default./.secrets/chain.pem